Thermal Management
Gap Filler
Heat Spreading

Short Introduction to Thermal Management
Thermal interface materials enhance heat transfer between components and heat sinks or metallic housings. Heat spreaders, made of graphite, distribute heat across a wider area, reducing hotspots. Gap fillers, typically soft, compliant materials, bridge uneven surfaces between components and coolers, improving thermal contact and minimizing total thermal resistance. Both types ensure efficient cooling and protect sensitive electronics from overheating.
Learn More About Thermal Management
-
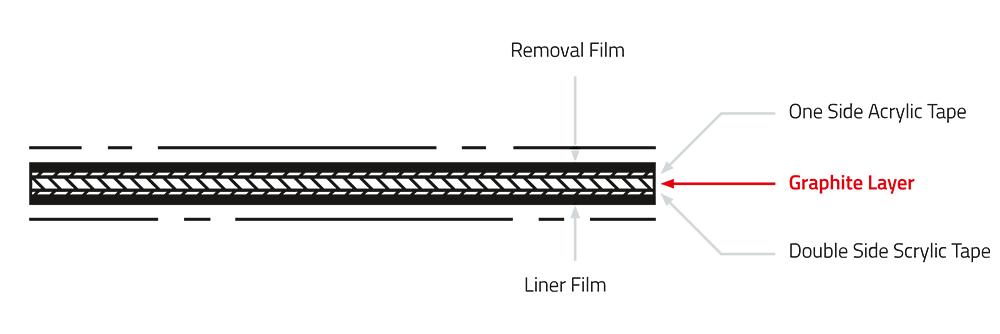
A graphite foil is a heat spreader made from synthetic graphite. This means that most of the thermal conductivity of the material is on the horizontal or XY axis. This effect allows the final application to utilize even larger cooling surfaces, rather than being limited by the contact surfaces of the component to be cooled. By wrapping the graphite around a foam core, it imparts vertical conductivity to a horizontal heat spreader.