Cable Solutions
Ferrites for Cable Assembly
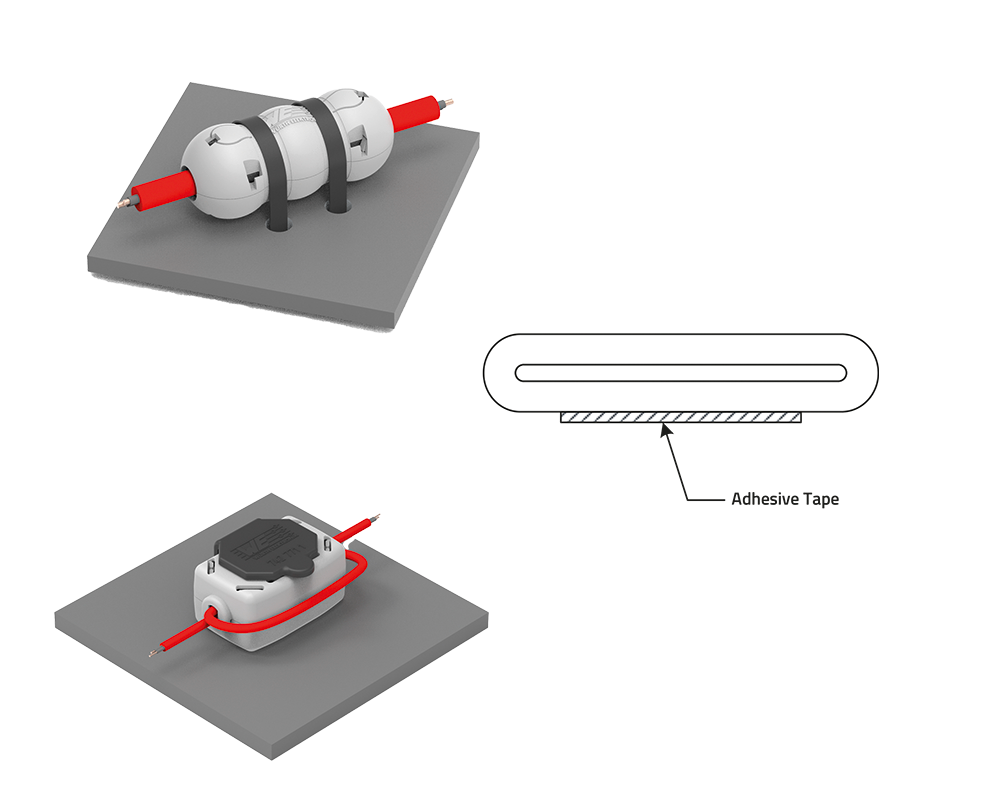
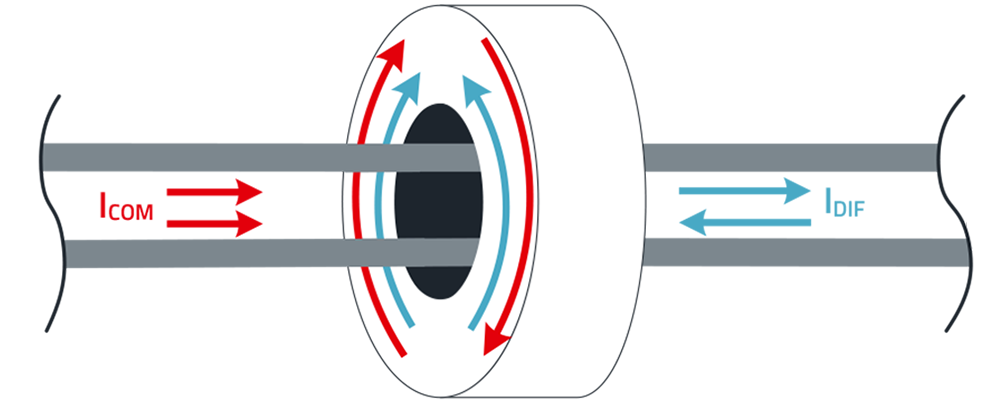
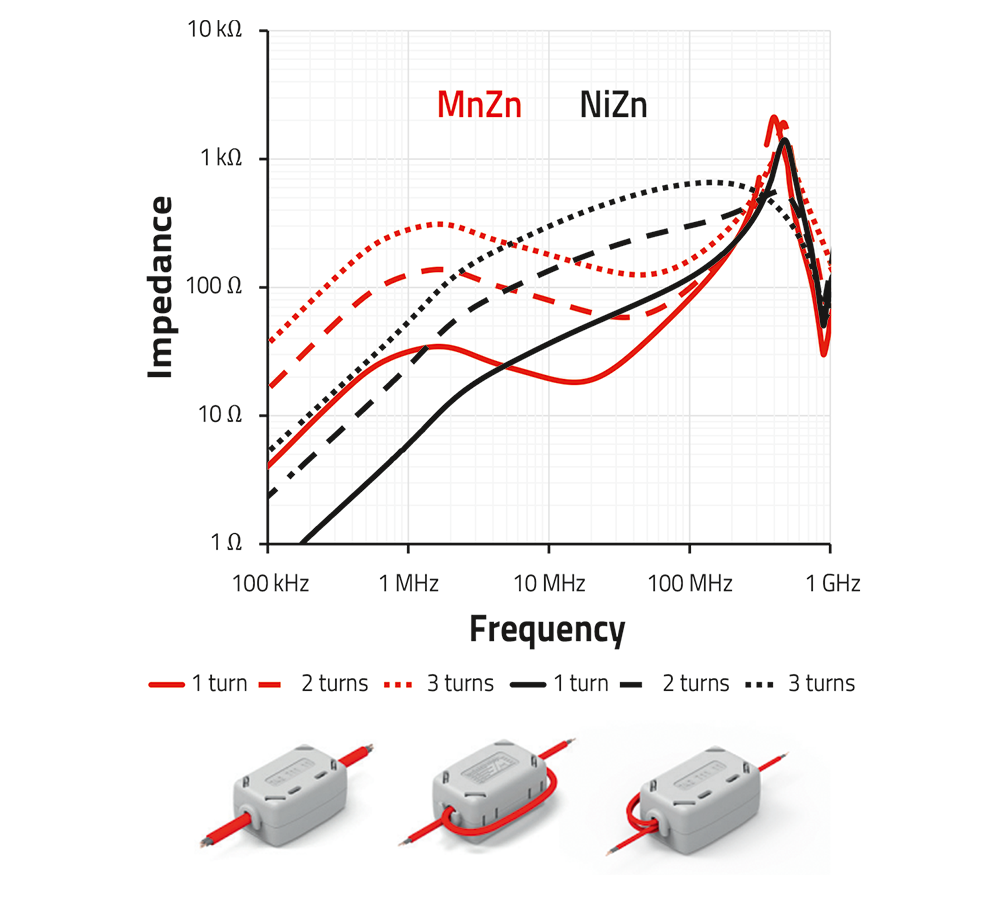
Ferrite cores and snap-on ferrites are designed to suppress EMI directly on the affected cable. They work by absorbing unwanted RF noise without affecting the useful signal. This makes them an easy and effective retrofit solution for improving EMC performance without altering the PCB.
Cable Shielding & Grounding
Shielding and grounding components provide a low-impedance return path for high-frequency noise on cable assemblies. This reduces emissions from the cable and protect cables from external interference.
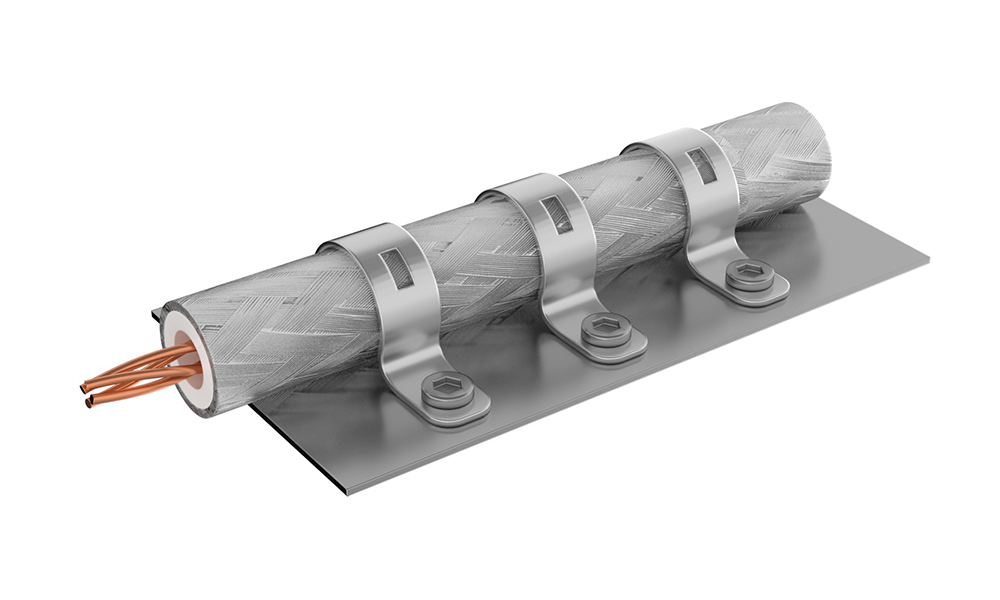
Cable Holders
Cable holders provide mechanical support and organized routing of wires and cables within a device. They prevent mechanical stress on solder joints and connectors by securing cables in place.

Short Introduction to Cable Solutions
Every conductor is an antenna. Therefore, it's important to anticipate radiated noise from the power cord or data cables and prevent coupling by applying the right cable ferrites. However, since cables act as antennas, their position on the PCB or layout within the housing has a great impact on their EMC behaviour. Cable holders and conductive shielding solutions ensure order and consistency in the placement of your cables.
Learn More About Cable Solutions
-
In cable shielding, it is important to have seamless shielding. A so-called pigtail can cause common-mode interference, which is generated by an RF voltage between the cable shield and the conductive housing.